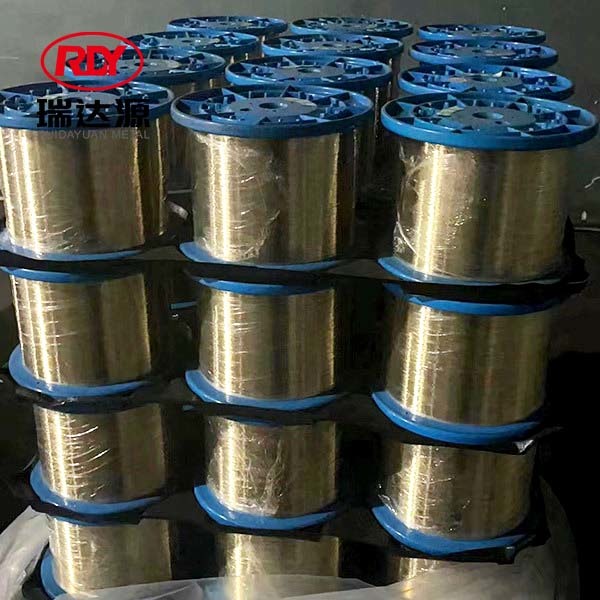
What is the hardness standard of galvanized iron wire?
Release Time:
Feb 13,2023
The hardness of galvanized iron wire is a common performance index of Z in the mechanical properties of metal materials. Hardness testing is also a fast and economical test method. However, there is no uniform and clear definition

The hardness of galvanized iron wire is a common performance index of Z in the mechanical properties of metal materials. Hardness testing is also a fast and economical test method. However, there is no uniform and clear definition of hardness of metal materials at home and abroad, including all test methods. Generally speaking, the hardness of metal is often considered as the resistance of material to plastic deformation, scratches, wear or cutting.
The hardness of galvanized iron wire is a common performance index of Z in the mechanical properties of metal materials. Hardness testing is also a fast and economical test method. However, there is no uniform and clear definition of hardness of metal materials at home and abroad, including all test methods. Generally speaking, the hardness of metal is often considered as the resistance of material to plastic deformation, scratches, wear or cutting.
During the commissioning of zinc dipping distance, keep the original speed unchanged, and determine the zinc dipping time (1) according to t=kd, where t is the zinc dipping time is constant, take 4-7d as the diameter of steel wire mm, and then estimate the zinc dipping distance. By adjusting the zinc dipping distance, the zinc dipping time of various specifications of steel wire is shortened by 5s on average compared with that before commissioning. See Table 1 for the results. In this way, the zinc consumption per ton of steel wire is reduced from 61kg to 59.4kg.
Hot galvanizing is dip plating in heated molten zinc solution, with fast production speed and thick but uneven coating. The market allows Z low thickness of 45 microns and Z high thickness of more than 300 microns. It is dark in color, consumes a lot of zinc metal, forms an infiltration layer with the base metal, and has good corrosion resistance. Hot galvanizing can be maintained for decades in outdoor environment.
Keywords:
Related news