Understanding Galvanized Iron Wire: Essential Insights for Construction Professionals
Release Time:
Jul 04,2025
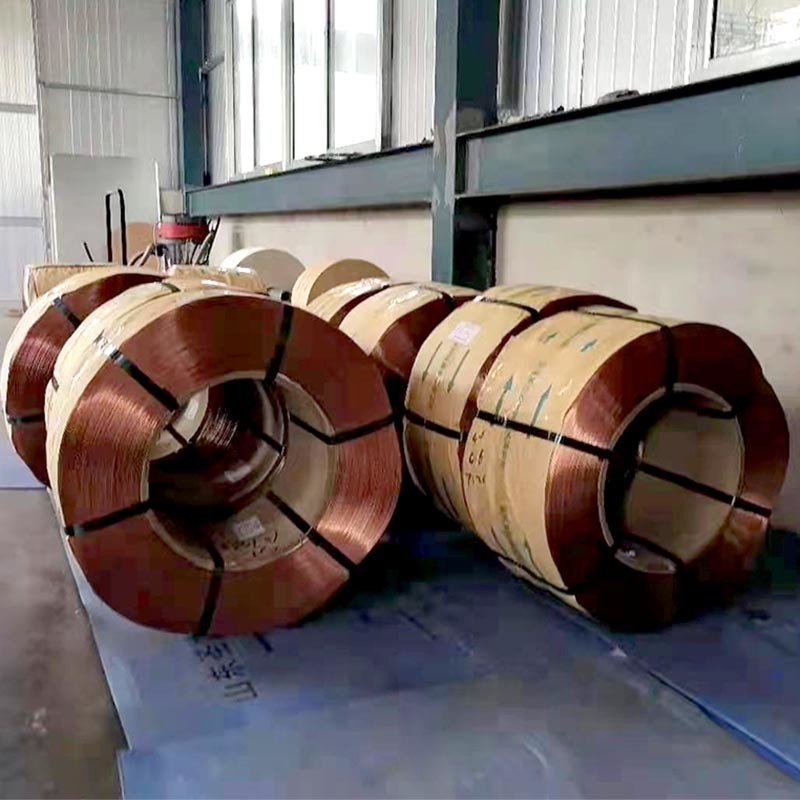
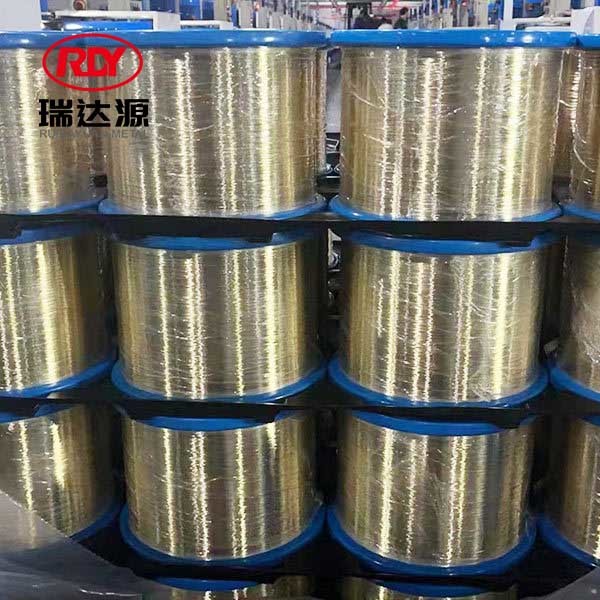
Galvanized iron wire is a versatile and widely used material in the construction and decoration sectors, primarily known for its strong resistance to corrosion. This wire is produced by coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc, which protects the underlying metal from environmental factors that typically lead to rust and degradation. Given the increasing focus on durability and sustainability in

Galvanized iron wire is a versatile and widely used material in the construction and decoration sectors, primarily known for its strong resistance to corrosion. This wire is produced by coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc, which protects the underlying metal from environmental factors that typically lead to rust and degradation. Given the increasing focus on durability and sustainability in construction, understanding the properties and applications of galvanized iron wire is crucial for professionals in the industry.
One of the key advantages of galvanized iron wire is its exceptional resistance to corrosion. The zinc coating serves as a sacrificial barrier, meaning it will corrode before the iron does. This characteristic significantly extends the lifespan of the wire, making it an ideal choice for outdoor applications, such as fencing, scaffolding, and wire mesh. In areas exposed to harsh weather conditions, galvanized iron wire often outperforms non-coated alternatives, minimizing maintenance costs and enhancing structural integrity.
In addition to its corrosion resistance, galvanized iron wire is known for its strength and flexibility. These properties allow it to be easily shaped and manipulated for various construction purposes. It is commonly used in the creation of reinforcement mesh, which is essential in concrete applications to provide additional tensile strength. Additionally, this wire can be utilized in the assembly of decorative elements, such as trellises and garden fences, where both functionality and aesthetic appeal are desired.
When selecting galvanized iron wire, professionals should consider several factors to ensure optimal performance. The gauge of the wire is an essential aspect, as it determines the wire's strength and flexibility. Thicker gauges are typically more robust but may be less flexible, while thinner gauges offer versatility but may lack strength for certain applications. Furthermore, the quality of the galvanization process can vary; therefore, it's essential to assess the coating's thickness and uniformity to ensure adequate protection against corrosion.
Another crucial aspect to keep in mind is the compatibility of galvanized iron wire with other materials. In some cases, contact with dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion, which may compromise the integrity of a construction project. Professionals should be diligent in selecting compatible materials to maintain the longevity of structures utilizing galvanized iron wire.
In conclusion, galvanized iron wire serves as a vital component in the construction and decoration industries, offering numerous advantages such as corrosion resistance, strength, and adaptability. By understanding its properties and applications, construction professionals can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and durability of their projects. Embracing the potential of galvanized iron wire can lead to more resilient structures and improved client satisfaction in an increasingly competitive market.
One of the key advantages of galvanized iron wire is its exceptional resistance to corrosion. The zinc coating serves as a sacrificial barrier, meaning it will corrode before the iron does. This characteristic significantly extends the lifespan of the wire, making it an ideal choice for outdoor applications, such as fencing, scaffolding, and wire mesh. In areas exposed to harsh weather conditions, galvanized iron wire often outperforms non-coated alternatives, minimizing maintenance costs and enhancing structural integrity.
In addition to its corrosion resistance, galvanized iron wire is known for its strength and flexibility. These properties allow it to be easily shaped and manipulated for various construction purposes. It is commonly used in the creation of reinforcement mesh, which is essential in concrete applications to provide additional tensile strength. Additionally, this wire can be utilized in the assembly of decorative elements, such as trellises and garden fences, where both functionality and aesthetic appeal are desired.
When selecting galvanized iron wire, professionals should consider several factors to ensure optimal performance. The gauge of the wire is an essential aspect, as it determines the wire's strength and flexibility. Thicker gauges are typically more robust but may be less flexible, while thinner gauges offer versatility but may lack strength for certain applications. Furthermore, the quality of the galvanization process can vary; therefore, it's essential to assess the coating's thickness and uniformity to ensure adequate protection against corrosion.
Another crucial aspect to keep in mind is the compatibility of galvanized iron wire with other materials. In some cases, contact with dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion, which may compromise the integrity of a construction project. Professionals should be diligent in selecting compatible materials to maintain the longevity of structures utilizing galvanized iron wire.
In conclusion, galvanized iron wire serves as a vital component in the construction and decoration industries, offering numerous advantages such as corrosion resistance, strength, and adaptability. By understanding its properties and applications, construction professionals can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and durability of their projects. Embracing the potential of galvanized iron wire can lead to more resilient structures and improved client satisfaction in an increasingly competitive market.
Keywords:
Related news